- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Iodine — The Thyroid’s Spark for Metabolism, Mood & Energy
Iodine enables T3/T4 production, shaping metabolism, body temperature, cognition, and mood. Below: quick self-check, story, expert dialogue, science, and FAQs.
✅ TL;DR — 3-Line Summary
- Iodine is essential for thyroid hormones that regulate metabolism, mood, and energy.
- A deficiency can quietly cause fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, and brain fog—especially in women.
- Learn to spot the signs and optimize intake through diet and smart choices. 🌊🧂
🧪 Self-Check: Are You Low on Iodine?
Answer all 10 items to get a tailored note. Educational only—not medical advice.
⏳ Analyzing your responses…
🧩 A Story You Might Relate To
“I Wasn’t Depressed — I Was Iodine Deficient.”
Maria, 34, gained weight despite eating clean, felt cold in summer, and battled brain fog. A full thyroid panel showed high TSH, low T3, and near-zero iodine.
“I didn’t even know iodine mattered after salt.” She switched to iodized sea salt, seaweed snacks, and targeted thyroid support. Energy returned, weight stabilized, and the fog lifted.
👩⚕️ Expert Dialogue: The Forgotten Nutrient for Modern Women
Dr. Tessa Lin, Endocrinologist:
“Iodine isn’t just a salt additive—it’s the spark for your thyroid system. Without it, your body can’t make T3 and T4.”
Dr. Lin: “Symptoms creep in: fatigue, constipation, dry skin, brittle hair, foggy mind. Raise iodine wisely and many feel better within weeks.”
Note: “Go slow—too much iodine too fast can backfire.”
🔬 The Science Behind Iodine & Your Thyroid
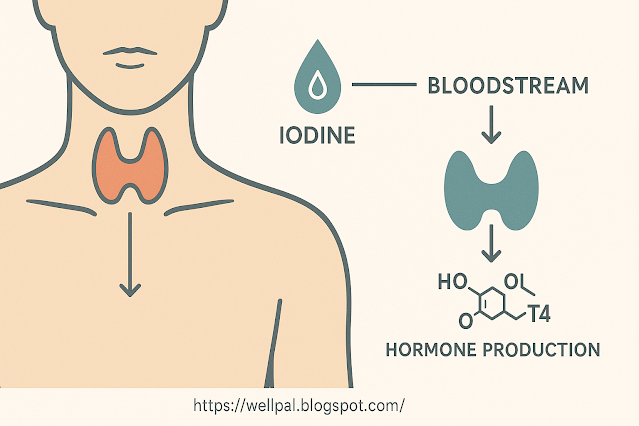
Iodine is a trace mineral that the thyroid uses to create thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), regulating:
- Metabolism and energy usage ⚡
- Body temperature 🌡
- Brain development & cognitive function 🧠
- Mood, motivation & focus 🧘♀️
- Hormonal balance (especially in women) 🩺
🚨 When iodine is low
- T3/T4 production drops → hypothyroid symptoms
- TSH rises → thyroid enlarges (goiter risk)
- Metabolism slows → weight gain, cold hands/feet, low energy
- Mood dips → depression, brain fog, anxiety
Even mild deficiency can affect fertility, child IQ, heart rate, menstrual cycles, and cholesterol.
📚 Scientific Sources
- World Health Organization (WHO): Iodine deficiency remains a global issue—even in developed countries.
- NIH Fact Sheet: Iodine — Health Professional
- Lancet Endocrinology (2021): Subclinical iodine deficiency linked to cognitive changes and hypothyroid symptoms.
📊 Quick Poll
Which symptom have you felt lately?
🤔 FAQ — Iodine Deficiency Explained
1) Can I get iodine without salt?
A: Yes. Seaweed (nori, kelp), seafood (cod, shrimp), dairy, and eggs are solid sources. Supplements can help if you only use sea salt.
2) What is the mild deficiency range?
A: WHO defines urinary iodine < 100 μg/L as mild deficiency; symptoms may appear even before labs drop significantly.
3) Is too much iodine dangerous?
A: Excessive intakes (>1,100 mcg/day) can suppress thyroid function. Avoid high-dose self-supplementation.
4) Is iodine important during pregnancy?
A: Absolutely—critical for fetal brain development and healthy thyroid hormones. Many prenatals include iodine, but not all.
5) I use sea salt—am I safe?
A: Most artisanal salts (Himalayan/Celtic) are not iodized. If you seldom eat seafood, consider iodized salt or seaweed.
🌟 Call to Action: Fuel Your Thyroid, Empower Your Body
- 🧂 Add iodized salt or seaweed snacks.
- 🐟 Enjoy seafood twice a week.
- 🩺 Ask your doctor about TSH/T3/T4 and iodine testing.
- 💊 Consider a low-dose iodine supplement if needed—go slow.
Educational content only; not medical advice.


Comments
Post a Comment